In today’s rapidly changing digital landscape, network connectivity is vital for effective communication and easy data transfer. Layer 2 vs Layer 3 is one of the most contentious issues in the IT world. While both layers serve distinct tasks, it is vital to understand their differences and select the best option for your individual requirements.
All About Layer 2 Connectivity: Data Link Layer
Layer 2, also known as the Data Link Layer, focuses on node-to-node data transfer within a network. It facilitates communication between devices by utilizing MAC (Media Access Control) addresses for identification. In a Layer 2 network, all nodes are visible to one another, enabling efficient data transmission.
One of the primary advantages of Layer 2 connectivity is its low latency. Since it requires fewer network hops compared to Layer 3, it is ideal for applications that demand real-time interactions, such as video conferencing or voice communication. Layer 2 connectivity, often associated with Ethernet, offers high network performance by utilizing the full bandwidth available.
Additionally, Layer 2 connectivity is relatively simple to configure and maintain. Unlike Layer 3, it eliminates the need for complex routing protocols and configurations, making it an attractive option for small to medium-sized businesses with limited IT resources.
All About Layer 3 Connectivity
Layer 3, also known as the Network Layer, focuses on routing data packets to specific nodes based on their IP addresses. Unlike Layer 2, Layer 3 connectivity provides point-to-point visibility among nodes. It is commonly used for wide area network (WAN) connectivity, connecting different LANs, and providing access to the internet.
Scalability is one of the major advantages of Layer 3 connectivity. It can handle large networks with numerous devices, making it suitable for complex network architectures. Layer 3 connectivity offers flexibility in terms of routing and network design, enabling efficient management of connections in globally distributed systems.
In terms of security, Layer 3 connectivity provides enhanced features such as firewalls and VPNs, which protect the network from external threats. Moreover, Layer 3 connectivity helps reduce network congestion by offering more efficient routing of network traffic, making it a preferred choice for managing connections in distributed networks.
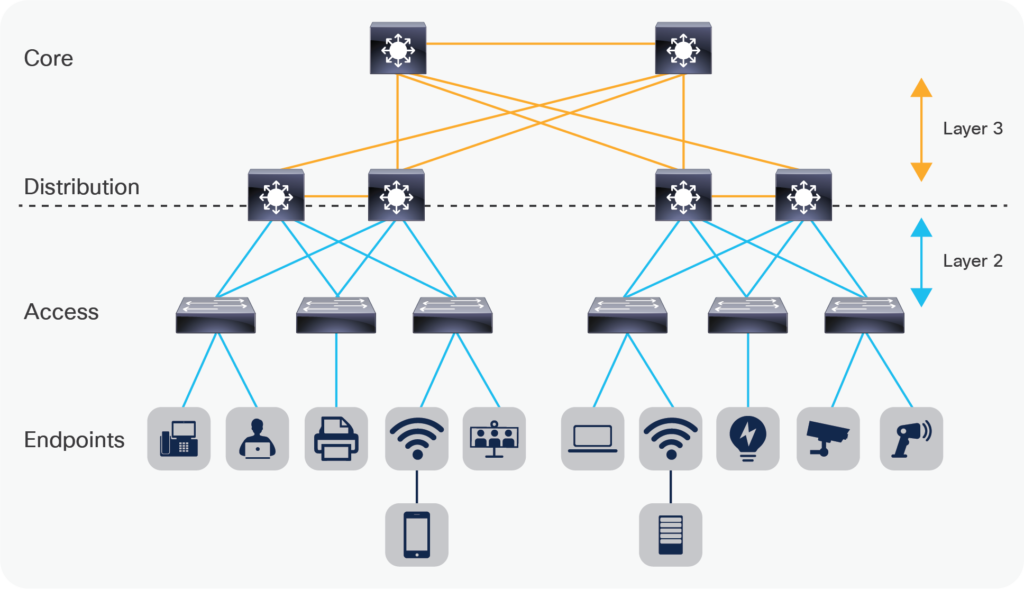
Layer 2 vs. Layer 3: Which Should You Use?
When planning your network infrastructure, the critical decision between opting for Layer 2 or Layer 3 connectivity hinges on the functionality and performance demands of your specific application or network. To make sure you’re making a smart choice, think about the following use cases that usually help people make this choice:
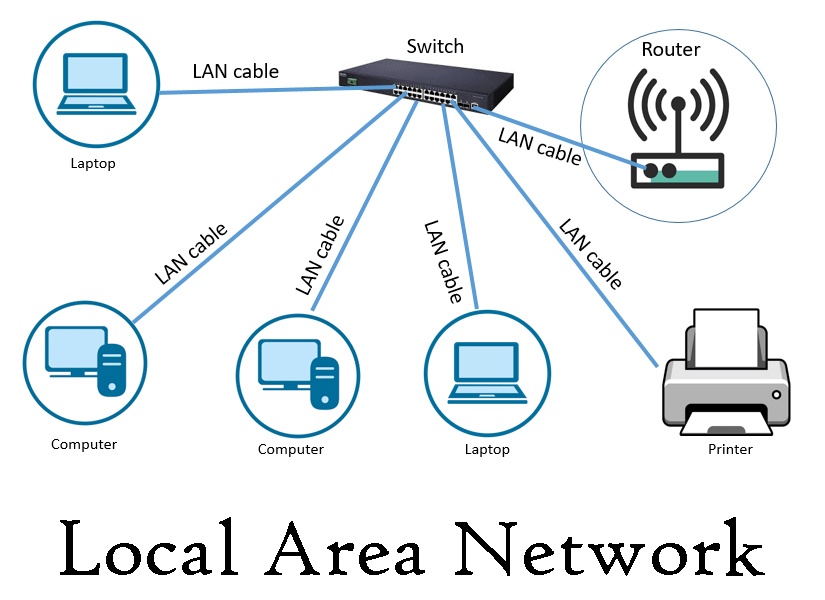
Local Network Connectivity
Within the confines of a local network setup, Layer 2 connectivity usually takes precedent due to several key advantages:
1.Low Latency: Layer 2 infrastructure offers minimal latency, which is crucial for applications requiring swift data exchange, such as live audio or video transmissions.
2. High Performance: By virtue of operating on the MAC level, Layer 2 can handle high-speed data transfer efficiently, which is advantageous for bandwidth-intensive applications.
3. Simplicity: Layer 2 provides straightforward connectivity that’s akin to extending an Ethernet cord between two points. This simplicity can facilitate easier maintenance and troubleshooting.
4.Real-time Applications: Due to its quick data forwarding capabilities, Layer 2 is favorable for real-time applications where any delay can significantly impact performance, such as VoIP or streaming.
5. Remote Support & Access: Providing a direct pipe for data, Layer 2 connectivity enables remote support and interaction with machines as if they were locally connected, which simplifies tasks like remote troubleshooting or file access.
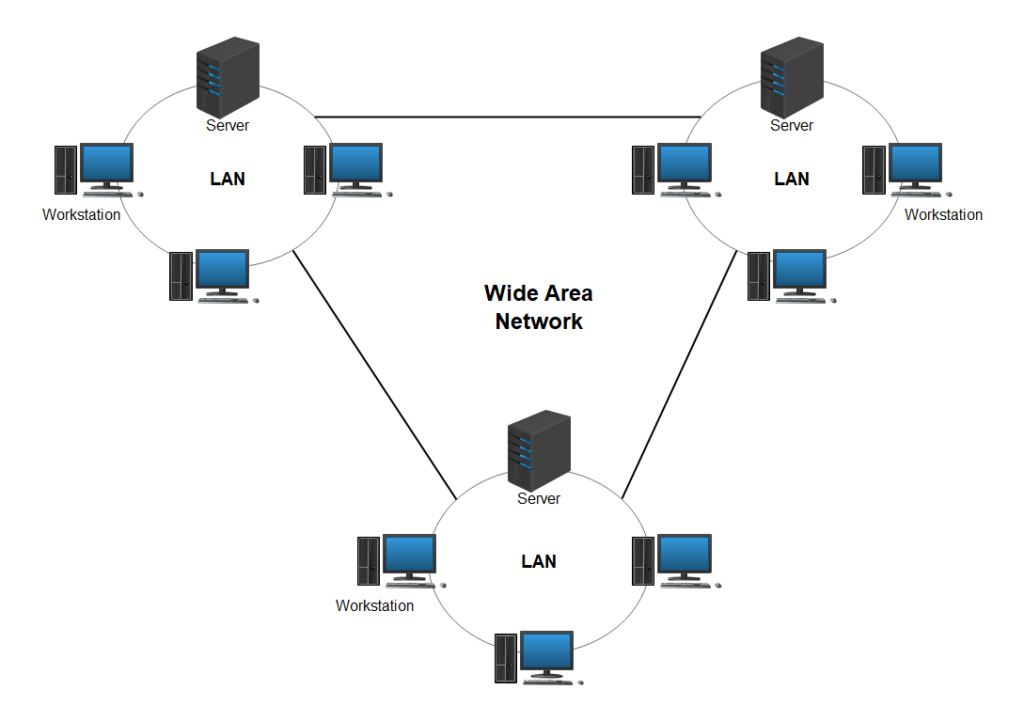
Wide-Area Network Connectivity
In scenarios where you are bridging the gap between geographically dispersed networks, Layer 3 connectivity becomes the favorable option:
- Scalability: As networks grow, so do their complexity and the size of their broadcast domains. Layer 3 networks are inherently scalable and can handle the growth without suffering from broadcast traffic issues that can plague large Layer 2 networks.
2. Inter-networking: Layer 3 is indispensable for creating internetworks – connecting various local networks (LANs) and facilitating access to the internet.
3.Enhanced Security: With Layer 3, you have more control over the data traffic, and the use of IP addresses can increase security measures through features like access control lists (ACLs).
4.Routing Strategies: Layer 3’s capability to support sophisticated routing strategies (like static and dynamic routing protocols) and services such as 1-1 NAT allows networks to be designed for efficiency, resiliency, and security.
5. Segmentation: Creating VLANs at Layer 2 is simple, but strategically using them with Layer 3 routing can yield a robust segmented network environment that reduces the size of broadcast domains and increases security by isolating network segments.
A hybrid method combining Layer 2 and Layer 3 connectivity may be best for many applications, balancing direct, high-speed local communications with route-optimized internetworking for comprehensive network capabilities.
In an organization with multiple departments that need high-speed access to shared local resources and secure and manage communications between their subnets and external networks, Layer 2 for local area connectivity and Layer 3 routing at the core can meet these needs.
Also Read: How to Reset Xfinity Router [Latest Updated]
In Closing
To make smart choices about network connection, you need to know all the differences about Layer 2 vs Layer 3. Layer 2 connectivity is good for both local network contact and remote support because it has low latency and is easy to use. Layer 3 connection, on the other hand, is perfect for wide-area network connectivity because it can be expanded, changed, and has better security features. By choosing the best network connectivity choice for your needs, you can make sure that communication works well, data transfers go smoothly, and the network runs at its best.