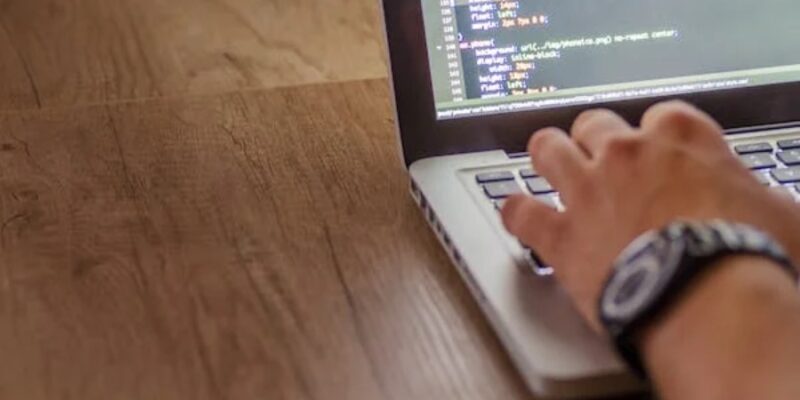
The virtual revolution has reshaped how we conduct business and our lives, and at the center of this modification lies the paradigm of cloud computing.
Among the diverse cloud computing models, Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) sticks out as a critical participant, supplying a bendy and scalable solution to satisfy the evolving wishes of individuals and groups.
In this comprehensive guide, we can delve into the intricacies of IaaS, exploring its definition, functionality, advantages, unusual use cases, key providers, protection considerations, demanding situations, and destiny traits.
What is Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)?
At its essence, IaaS is a cloud computing provider that offers virtualized computing assets over the net.
Unlike conventional IT infrastructure, where physical servers and hardware are maintained on-site, IaaS permits users to gain access to and control computing resources remotely.
This model allows for extra flexibility and efficiency in helpful resource usage.
How Does IaaS Work?
- Virtualization Technology
One of the essential additives of IaaS is virtualization technology. This generation allows the creation of virtual instances of computing resources, including servers, storage, and networks.
These virtualized assets can be scaled up or down without difficulty based on a call, presenting a dynamic and responsive infrastructure.
- Resource Management
IaaS platforms such as Gcore Cloud and Google Cloud offer robust aid control skills, allowing customers to allocate and deallocate sources.
This ensures top-quality utilization of computing electricity and prevents unnecessary prices associated with idle resources.
- Scalability and Flexibility
Scalability is a defining function of IaaS. Users can scale their infrastructure vertically by increasing the computing power of personal components or horizontally by including more additives.
This flexibility allows groups to evolve to changing workloads and demands effectively.
Advantages of Using IaaS
- Cost Efficiency
One of the number one advantages of IaaS is fee efficiency. By leveraging virtualized sources and purchasing utilization on a pay-as-you-cross basis, corporations can considerably lessen capital costs related to retaining physical infrastructure.
- Scalability
The scalability of IaaS lets groups grow without the need for widespread advanced investments.
Whether dealing with accelerated user site visitors, increasing records garages, or enhancing processing abilities, IaaS offers essential infrastructure on demand.
- Resource Management
IaaS structures frequently come with intuitive management interfaces that empower customers to effectively reveal and manipulate their assets. This degree of management enhances resource optimization and streamlines universal operations.
- Accessibility and Flexibility
IaaS removes geographical constraints, imparting customers with faraway access to their infrastructure.
This accessibility benefits dispensed groups, far-off employees, and international organizations seeking unified and reachable IT surroundings.
Everyday Use Cases for IaaS
- Development and Testing Environments
IaaS is ideal for creating and dealing with improvement and checking out environments. Developers can quickly provision digital times for checking out applications, ensuring an unbroken and green improvement lifecycle.
- Hosting Websites and Applications
Many companies leverage IaaS for web hosting websites and packages. The scalable nature of IaaS comprises varying stages of visitors and ensures ideal performance without the want for extensive infrastructure investments.
- Data Storage and Backup
IaaS excels in imparting dependable and scalable information garage solutions. Organizations can securely store and back up significant volumes of facts without the limitations of physical storage obstacles.
IaaS Providers
- Market Leaders
Several prominent IaaS providers dominate the market, supplying several offerings. Amazon Web Services (AWS), Gcore Cloud, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) are the various vital gamers, each with its strengths and particular features.
- Factors to Consider When Choosing an IaaS Provider
When deciding on an IaaS issuer, factors including overall performance, reliability, security capabilities, and pricing fashions must be carefully evaluated.
Understanding the precise wishes of your organization will guide you in choosing the company that aligns excellently with your necessities.
Security Considerations
- Data Encryption
Ensuring the safety of information is a paramount subject in cloud computing. IaaS providers implement robust encryption protocols to safeguard data during transmission and storage, mitigating the hazard of unauthorized entry.
- Compliance and Certifications
Compliance with industry guidelines and acquiring applicable certifications are essential for IaaS security.
Reputable companies adhere to industry standards, assuring users that their infrastructure meets the critical security and privateness requirements.
- Shared Responsibility Model
Security in IaaS follows a shared obligation version, where the company and the person have roles in maintaining secure surroundings.
Understanding those duties is crucial for implementing robust security measures.
Future Trends in IaaS
- Edge Computing
The upward push of area computing is poised to reshape the landscape of IaaS. Edge computing brings computational power closer to the data supply, decreasing latency and improving actual-time processing abilities.
- Integration with Emerging Technologies
IaaS is becoming increasingly integrated with rising technology, including synthetic intelligence, gadget mastering, and the Internet of Things (IoT).
This integration enhances the competencies of IaaS platforms, enabling users to harness the power of present-day technologies.
- Sustainable Computing Practices
As environmental issues end up being extra-reported, IaaS vendors are adopting sustainable computing practices.
This includes optimizing strength consumption, utilizing renewable sources, and imposing green data middle designs.
Conclusion
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is a cornerstone of present-day cloud computing, offering a dynamic and scalable answer for various computing wishes.
Understanding the key components, blessings, use instances, providers, protection considerations, challenges, and destiny trends in IaaS is essential for people and companies searching to navigate the complexities of the virtual generation.
Embracing the capacity of IaaS can result in enhanced performance, flexibility, and innovation within the ever-evolving landscape of the information era.