The financial world is a giant and dynamic one. In such a world, distinguishing between private equity and venture capital is crucial. Aside from that, this goes without saying that you need to teach yourself many stuff about the financial market. You need these knowledge even if you are not a trader. But if you are on or are planning to invest in anything, these are crucial for you.
In this article we’ll delve into the realms of these investment strategies. Then, we’ll also explore their definitions, advantages, drawbacks, and the critical differences that set them apart. After doing that, you would become more ready to work or understand the financial markets.
What is Private Equity?
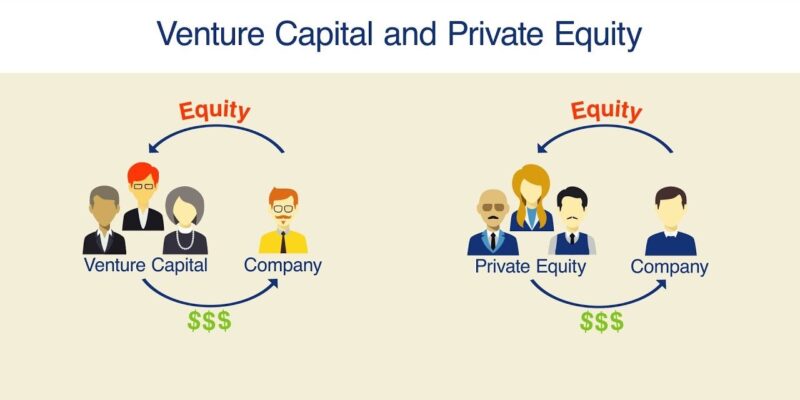
Private equity represents a form of investment where funds are pooled to acquire, invest in, or fund various businesses. These investments are typically made in established companies with the goal of restructuring, improving efficiency, and eventually selling for a profit. Private equity firms often wield considerable influence over the companies they invest in.
They will be doing this while implementing changes to enhance performance and value. For example, look at iconic deals such as the acquisition of Dell by Silver Lake Partners or the takeover of Heinz by Berkshire Hathaway. Also 3G Capital showcases the significant impact private equity can have on well-established enterprises.
Pros and Cons of Private Equity
Private equity offers notable advantages, such as the potential for substantial returns and the injection of expertise to revitalize struggling businesses. However, it comes with its share of challenges. The prolonged investment horizon and the risk of conflicts between investors and existing management are among the downsides. Additionally, the high level of debt often used in these transactions can pose financial risks.
Pros:
1.High Returns:Private equity investments have the potential for substantial returns, especially when successful operational improvements are implemented.
2. Operational Control: Investors in private equity often have significant control over the companies they invest in, allowing for hands-on management and strategic decision-making.
3. Diversification: Private equity provides diversification within a portfolio, as investments can span various industries and sectors.
4. Long-Term Focus: Private equity firms typically have a longer investment horizon, allowing for patient capital and strategic planning.
5. Stabilizing Effect: In economic downturns, private equity can provide stability, as the focus on operational improvement can insulate businesses from market volatility.
Cons:
1. Illiquidity: Investments in private equity are often illiquid, with capital tied up for an extended period, limiting liquidity for investors.
2. High Entry Barriers: Access to private equity investments is often restricted to institutional investors and high-net-worth individuals, creating barriers for smaller investors.
3. Market Dependency: Private equity returns can be influenced by broader economic conditions, making them susceptible to market fluctuations.
4. Management Conflicts: There is potential for conflicts of interest between private equity investors and existing management, particularly when implementing changes.
5. High Leverage Risks: The substantial use of debt in private equity transactions can amplify risks, especially during economic downturns.
Now that you have learned what Private Equity is, it’s time to learn about Venture Capital.
What is Venture Capital?
Venture capital, on the other hand, is a form of financing primarily dedicated to startups and small businesses with high growth potential. Venture capitalists invest in these early-stage companies in exchange for equity, providing not just funds but also mentorship and strategic guidance. Success stories like Google and Facebook attribute their initial growth to venture capital funding.

Pros and Cons of Venture Capital
Venture capital plays a pivotal role in nurturing innovation and supporting the growth of startups. However, the high-risk nature of early-stage investments means that not all ventures succeed. Additionally, the process of securing venture capital can be time-consuming and competitive, and founders often have to relinquish a significant portion of control over their companies.
Pros:
1. Innovation Support: Venture capital fosters innovation by providing funding and mentorship to early-stage companies with disruptive ideas.
2. Potential for High Returns: Successful investments in high-growth startups can yield significant returns, surpassing those in more traditional investment avenues.
3. Diverse Portfolio: Venture capital allows for diversification, enabling investors to spread risk across a range of startups and industries.
4. Entrepreneurial Ecosystem: VC contributes to the development of entrepreneurial ecosystems by supporting the growth of startups and fostering a culture of innovation.
5. Job Creation: Investments in startups often lead to job creation, contributing positively to economic development.
Cons:
1. High Failure Rate: Many startups funded by venture capital fail, leading to a high-risk environment and potential loss of invested capital.
2. Long Time to Liquidity: It can take several years for venture capital investments to yield returns, and exits through IPOs or acquisitions may be delayed.
3. Limited Control: VC investors often have limited control over the management and strategic decisions of the startups they invest in.
4. Market Sensitivity: Venture capital returns can be sensitive to market conditions, making them vulnerable to economic downturns.
5. Intense Competition: The pursuit of promising startups can lead to fierce competition among venture capitalists, potentially affecting investment opportunities and valuations.
Private Equity vs. Venture Capital
Here we want to put private equity vs venture capital to find out their differences. Then, let’s not waste any time and get to discuss the differences in private equity vs venture capital.
While both private equity and venture capital involve investing capital in companies, they differ in terms of the stage of the businesses they target. Private equity focuses on mature companies, aiming for operational improvement and profitability. Whereas venture capital targets startups with promising potential for growth. The risk-return profiles and investment strategies of these two forms of financing vary significantly.
Private equity and venture capital, despite sharing the overarching goal of generating returns for investors, diverge in their approaches. Private equity thrives on the acquisition of established businesses, often implementing operational changes to increase efficiency and profitability.
In contrast, venture capital embraces the uncertainty of early-stage ventures, nurturing innovation and providing crucial support during the nascent phases of a company’s development. Choosing between the two depends on factors like the maturity of the target business and the investor’s risk appetite.
Private Equity vs. Venture Capital Salaries
One critical aspect that differentiates private equity and venture capital is the compensation structure. But if we want to compare the two we have to also discuss private equity vs venture capital salaries. Then, let’s continue putting private equity vs venture capital to find the one that fits your needs.
Professionals in private equity often receive a substantial portion of their compensation in the form of carried interest, a share of profits earned from successful investments. This aligns their interests closely with the success of the investments. In venture capital, the compensation structure may include a management fee and a share of the fund’s profits. Salaries in both sectors can be lucrative, but the specific structure reflects the unique risk and reward dynamics associated with each investment strategy.
Conclusion
Understanding private equity and venture capital is essential for investors, entrepreneurs, and anyone navigating the world of finance. Private equity’s focus on mature businesses and operational restructuring contrasts with venture capital’s emphasis on early-stage innovation. Each avenue has its merits and challenges, offering distinct opportunities for investors and businesses alike. Whether it’s the seasoned stability of private equity or the risk-laden excitement of venture capital, recognizing the differences allows stakeholders to make informed decisions in their pursuit of financial success.
FAQ
- Who makes more money private equity or venture capital?
Private equity professionals often earn more money than those in venture capital due to the nature of their investments. The compensation structure, including carried interest, aligns their earnings closely with the success of their investments. This can potentially lead to substantial profits for both the investor and the company they invest in.
- Is private equity a type of VC?
No, private equity is not a type of venture capital. While both involve investing capital in companies, they differ in their focus. Private equity targets mature businesses, aiming for operational improvement, while venture capital focuses on early-stage ventures with high growth potential. Then, they differ in their approach to problems and though have different outcomes.
- Which is riskier, private equity or VC?
Venture capital is generally considered riskier than private equity. VC investments are in early-stage companies with uncertain futures, posing a higher risk of failure. Private equity, dealing with more established businesses, carries different risks, often associated with market conditions and operational improvements.