As data has been commonly called the new oil in this age of artificial intelligence and machine learning technology, we must protect these valuable assets from our hazy memories pinned in pictures and videos to official critical business resources and big information databases. Whatever the data you possess or create, it’s loss never intended. The 3-2-1 Backup Strategy is one of the most popular ways at the top to backup data safely. This post will tackle the 3-2-1 backup strategy, what the strategy involves, how effective it is, and its successful implementation.
What Is the 3-2-1 Backup Strategy?
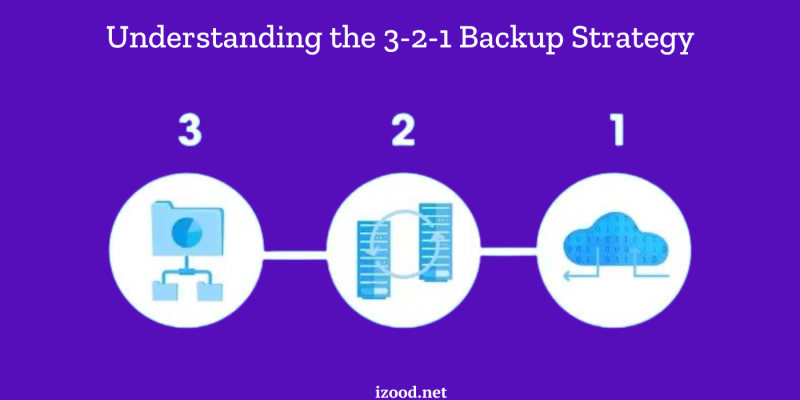
The 3-2-1 backup strategy is an old but effective one. It has saved many organizations from catastrophic data loss over the decades. The basic idea is simple enough:
- Retain three copies of your data.
- Add two copies on different media types.
- Keep a copy off-site.
This method is so popular due to its simplicity and strength, as with this attacker’s multiple layers of security mechanisms.
3-2-1 Backup Rules
- Three Copies of Data: Having three copies is better. With three copies, if one is lost, damaged, or corrupt, a second copy can be used. These three copies are usually the primary data with two additional backups.
- Two Different Media Types: Store multiple media backups to keep your original data backed up to avoid the risk. Use internal hard drives, external hard drives, disks, USB drives, etc.
- One Off-Site Copy: At a minimum, one copy should be kept off-site to prevent total loss in the case of local disasters (fires, floods, theft). This off-site copy can be additional cloud-based data or physically located somewhere other than the primary digital storage location.

How is a 3-2-1 Backup Strategy Effective?
The 3-2-1 backup strategy helps to secure your data with its layered approach. This is safer, as there are various risks when keeping copies on only one kind of media in one place. For instance, if your backups are on more than one type of media (hard drives plus USBs), how likely is it that all disks will fail or be damaged simultaneously? One copy off-site means that if anything happens at your primary location, like power loss, fire, or flooding, you have your data saved. It also allows that if you ever delete or corrupt a file, it could pull from other backups. Because this method can particularly prevent any threat, it is not wrong to use it for securing your data, which may give you satisfaction in a manual way at the same time and ensure maximum level security layering different from each plain key used through a callback.
Variations of the 3-2-1 Backup Methodology
The 3-2-1 backup strategy is solid enough, but there are variations on it to cater to numerous specific needs:
- 3-2-2 Strategy: Same as 3-2-1, but adds another off-site backup. This variation adds an extra layer of protection and is preferred for companies with important data.
- 3-2-1-1-0 Strategy: This strategy is used with business-critical data, and it is more advanced. It includes three copies of the data, two different media types, one off-site copy of the backups for disaster recovery (recommended to be offline), and zero errors during verification. This is a compelling way to protect against ransomware and maintain data integrity.
How to Get the Third Copy of Data Off-Site
There are several methods to ensure an off-site copy:
- Cloud Storage: These tools like Google Drive, Dropbox, and Amazon s3 offer security for off-site storage solutions with easy access and scalability.
- Physical Transport: Regular physical media like external hard drives in another place can be considered an off-site backup.
- Data Centers: The cost is often high, but data centers are very secure and provide reliable off-site storage infrastructure.
Universality of the 3-2-1 Backup Rule
The 3-2-1 backup rule is universal and works in any context. Individuals can use it to protect family photos and videos, important files or folders, or other personal data. Small businesses use it to protect the client base, information about services, business work, and financial reports. It makes it possible to ensure the continuity of the company’s business. Large enterprises use the 3-2-1 backup rule to protect the data about many customers, information about intellectual property, and business applications. Therefore, the 3-2-1 backup rule includes the best practices for protecting data at all levels.
Do New Uses of Backup Data Make the 3-2-1 Rule Ineffective?
Data times have changed, and with that change comes new struggles that can affect the effectiveness of 3-2-1 backup rule. With the pace at which data is accumulating, managing and storing duplicate copies has become exponentially more complicated and costly. The emerging dependence on cloud storage has also somewhat deteriorated security if handled carelessly. New uses include analytics and real-time access to backup data, which have driven the need for quicker recovery processes. While the challenges of this rule continue to pop up, its critical core principles still hold. This solution should protect your data well by adapting the strategy to suit our current needs, including cutting-edge security or bolstering storage capability.
What are the Challenges of 3-2-1 Backup?
Implementing the 3-2-1 backup strategy comes with challenges:
- Cost: Maintaining lots of copies for a great amount of data can be quite expensive.
- Management Complexity: Bringing all types of media together, plus an idea like off-site storage, is managed responsibly.
- Data Integrity: Regularly maintaining, checking and verifying your backups is a man in the middle to stop data loss.
How to Successfully Implement a 3-2-1 Backup Strategy
- Assess Your Needs: Evaluate how much your data is critical and what type level of backup you require
- Choose Media Types: It is important that your backups have some diversity in media types and that you use a reliable source.
- Automate Backup Processes: Utilize software solutions to automate backups, significantly decreasing the potential for human error and maintaining consistency.
- Regularly Test Backups: Test your backups regularly to ensure they can fully restore data.
- Secure Off-Site Storage: Select a secure off-site storage solution that physically stores these backups in the cloud or some other form for disaster recovery.
Conclusion
Although the 3-2-1 backup strategy is not new, it is the foundation of data protection. The ease and several layers with which data safety is guaranteed underscores its effectiveness. Although challenges and modifications have been made to how the data is described, maintaining and changing with the 3-2-1 ensures that the data protection is robust. Whether for personal use or continued business, investing in 3-2-1 data backup is a sound decision to secure the data from loss and disasters.

![How to Pause Location on Find My iPhone Without Them Knowing? [2024] 18 how to pause location on find my iphone](https://izood.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/10/How-to-Pause-Location-on-Find-My-iPhone-Without-Them-Knowing-400x300.png)

![How To Inspect Element on iPhone [4 Methods] 21 how to inspect element on iphone](https://izood.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/10/how-to-inspect-element-on-iphone-3-400x300.png)